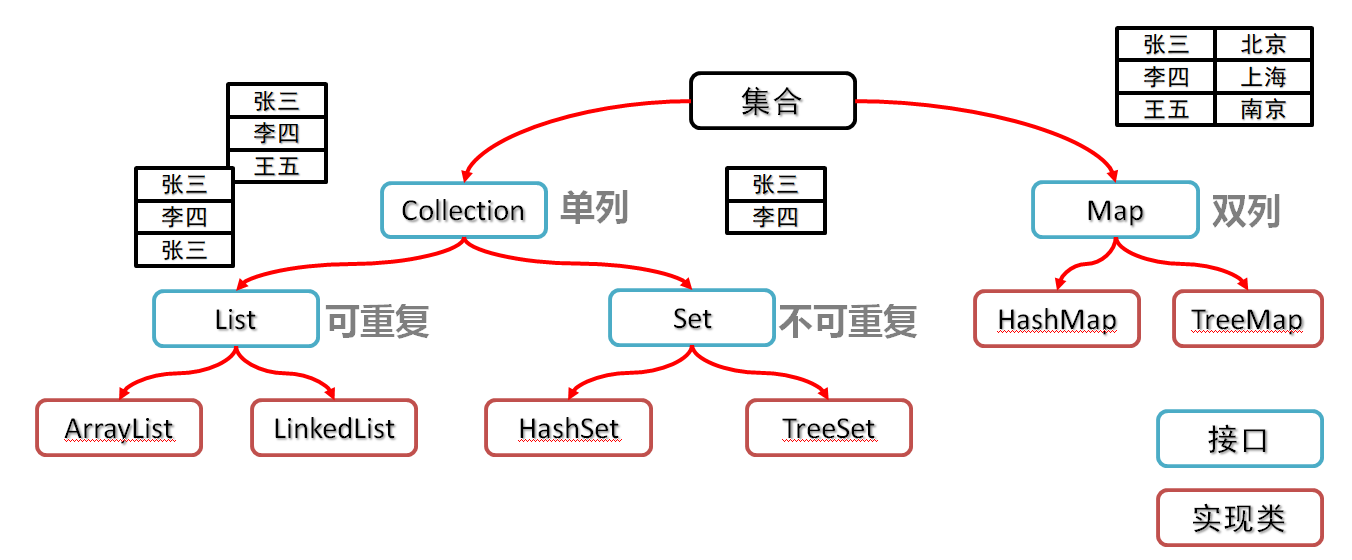
Java
双列集合Map
双列集合特点:
- 一次需要存储一对数据, 分别为键和值
- 键不能重复, 值可以
- 键和值一一对应, 通过对应的键找到对应的值
Map常用方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
put(K key, V value) | 向集合中添加元素 |
get(Object key) | 根据key获取value |
remove(Object key) | 根据key删除元素, 返回被删除的value |
containsKey(Object key) | 判断集合中是否存在某个key |
containsValue(Object value) | 判断集合中是否存在某个value |
size() | 获取集合中元素的个数 |
isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
clear() | 清空集合 |
keySet() | 获取所有key的集合 |
values() | 获取所有value的集合 |
entrySet() | 获取所有key-value的集合 |
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//因为Map是一个接口, 所以想要使用, 需要对应的实现类, 完成接口多态
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("wang", 21);
map.put("jia", 22);
map.put("nian", 23);
System.out.println(map);// {jia=22, wang=21, nian=23}
map.put("wang", 24);
System.out.println(map);// {jia=22, wang=24, nian=23}
}
}提示
在双列集合中使用put(), 若键不存在于双列集合会直接添加; 而put()的键重复时, 会覆盖之前的值.
遍历方式
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//遍历map集合
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("wang", 21);
map.put("jia", 22);
map.put("nian", 23);
//遍历方式1 键找值
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
//通过key拿到value
int value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
//遍历方式2 键值对
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
String key = entry.getKey();
int value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
//遍历方式3 匿名内部类
map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(String key, Integer value) {
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
});
//lambda表达式
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
);
}
}HashMap
- HashMap是Map的实现类
- 没有额外的学习特有方法, 直接使用Map的方法就行
- 底层基于哈希表
底层原理
底层原理基本与HashSet一致, 但有下列两个特点
- 在比较时, 比较的是
key值 - 如果
key重复, 则覆盖之前的value
提示
HashMap底层基于哈希表- 依赖
hashCode()和equals()方法保证键唯一 - 如果键存储的是自定义对象, 需要重写
hashCode()和equals()方法; 如果值存储的是自定义对象, 不需要重写hashCode()和equals()方法
LinkedHashMap
- 特点: 由键决定: 有序, 不重复, 无索引
- 有序指的是, 取出的顺序和添加顺序一致
- 底层原理: 基于哈希表和双链表
java
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<>();
lhm.put("zhangsan", 23);
lhm.put("lisi", 24);
lhm.put("wangwu", 25);
lhm.put("wangwu", 29);
System.out.println(lhm);// {zhangsan=23, lisi=24, wangwu=29}
lhm.remove("lisi");// {zhangsan=23, wangwu=29}
System.out.println(lhm);
}
}TreeMap
- 特点: 由键决定: 可排序, 不重复, 无索引
- 底层原理: 基于红黑树
- 键必须实现
Comparable接口, 并且重写compareTo()方法 - 注: 默认按照键从小到大进行排序, 也可以自己制定规则
java
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, "A");
map.put(4, "D");
map.put(2, "B");
map.put(3, "C");
System.out.println(map);// {1=A, 2=B, 3=C, 4=D}
TreeMap<String, Integer> map1 = new TreeMap<>();
map1.put("A", 1);
map1.put("D", 2);
map1.put("B", 3);
map1.put("C",4);
System.out.println(map1);// {A=1, B=3, C=4, D=2}
}
}提示
默认按照键从小到大进行排序, 比较规则与TreeSet一致
Properties
此集合需学完IO流之后更好理解
- 双列集合, 常用于配置文件当中
- 配置文件: 在
Java中配置文件以.properties后缀结尾
常用方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
put(Object, Object) | 将键值对添加到Properties集合中 |
setProperty(String, String) | 将键值对添加到Properties集合中 |
getProperty(String) | 根据键获取值 |
store(OutputStream, String) | 将Properties集合中的数据存储到配置文件当中 |
load(InputStream) | 加载配置文件, 将配置文件中的数据存储到Properties集合中 |
remove(Object) | 删除键值对 |
list(PrintStream) | 将Properties集合中的键值对输出到指定的流中 |
写入数据
java
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.put("111", "222");
prop.setProperty("search", "true");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("puzzlegame\\a.properties");
//写入文件
prop.store(fw, "test");
System.out.println(prop);
fw.close();
}
}properties
#test
#Sat Nov 16 12:06:23 CST 2024
111=222
search=true读取数据
java
public class PropertiesDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//常用与配置文件当中
Properties prop = new Properties();
FileReader fr = new FileReader("puzzlegame\\a.properties");
prop.load(fr);
//{111=222, search=true}
System.out.println(prop);
}
}