Java
异常体系结构
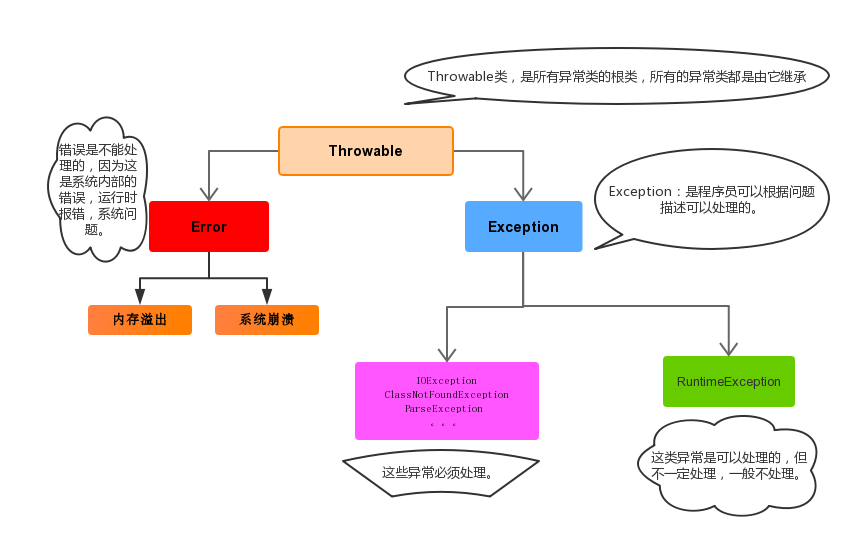
java.lang.Error:一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理java.lang.Exception:可以进行异常的处理- 编译时异常(checked)
IOExceptionFileNotFoundExceptionClassNotFoundException
- 运行时异常(unchecked,RuntimeException)
- NollPointerException
- ArrayIndexOutBoundsException
- ClassCatsException
- InputMismatchException
- ArithmeticException
2.从程序执行过程,看编译时异常和运行时异常
编译时异常:执行javac.exe命令时,可能出现的异常
运行时异常:执行java.exe命令时,出现的异常
异常处理
1. java虚拟机处理
程序在正常执行的过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象。并将此对象抛出。一旦抛出对象以后,其后的代码就不在执行, 并且使用红色字体输出异常信息。
关于异常对象的产生:
系统自动生成的异常对象 手动的生成一个异常对象,并抛出throw
危险
java
int[] array = {1,2,3};
// 数组越界
System.out.println(array[10]);Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 10 out of bounds for length 3
手动捕获抛出异常
- 抛出异常:
throw new 异常类 - 捕获异常:
try...catch
try...catch
java
try {
//可能出现异常的代码
} catch(异常类型1 变量名1) {
//处理异常的方式1
} catch(异常类型2 变量名2) {
//处理异常的方式2
} catch(异常类型3 变量名3) {
//处理异常的方式3
} finally {// 可选
//一定会执行的代码
}提示
如果try中出现了异常, 就会被catch给捕获
代码演示
java
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要求: number的长度小于等于10位, 将类型String转换为int类型
try {
//可能出现异常的代码
int result = method("1d3");
System.out.println(result);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
//注: 异常的子类要在前, 如果父类在前, 则子类无法捕获到异常, 因为父类能捕获到所有子类的异常
System.out.println("number数据不合法");
} catch (RuntimeException e) {// 父类在后
//手动处理异常问题
System.out.println("number的长度小于等于10位");
}
}
public static int method(String number) {
if(number.length() > 10) {
//可能出现的错误1 RuntimeException
throw new RuntimeException();
}
//可能出现的错误2 NumberFormatException
return Integer.parseInt(number);
}
}提示
异常的子类要在前, 如果父类在前, 则子类无法捕获到异常, 因为父类能捕获到所有子类的异常
自己处理可能出现的问题
- 如果try中的没有遇到问题, 怎么执行?
- 则不会执行catch里面的语句, 并且继续向下执行代码
- 如果try中遇到了多个问题, 怎么执行?
- 当抛出一个异常之后,
try中的代码就不再执行, 而是跳转到catch中去执行
- 当抛出一个异常之后,
- 如果try中遇到的问题没有被捕获, 怎么执行?
- 则此异常会被java虚拟机处理, 并且输出异常信息
- 如果try中遇到了问题, 那么try下面的代码会执行吗?
- 不会执行
异常中的或运算符
|: 或运算符, 表示或的关系, 如果多个异常处理的方式一样, 则可以使用或运算符
java
public class Demo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String[] arr = {"1", "2", "3"};
String str = arr[10];
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | NumberFormatException e) {
//如果多个异常处理的方式一样, 则可以使用或运算符
System.out.println("数据非法");
}
}
}throw 和 throws
- throw: 抛出异常
- throws:
throws 异常类型, 异常类型,...写在方法的声明处。表示此方法执行时,可能会抛出的异常类型。
一旦方法体执行时,出现异常,仍会在异常代码处生成一个异常类的对象,此对象满足throws后异常类型时,就会被抛出。异常代码后续的代码,就不再被执行。
java
//NumberFormatException是运行时的异常, 运行异常可以手动不写
public static int method(String number) /* throws NumberFormatException */ {
if(number.length() > 10) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
return Integer.parseInt(number);
}提示
运行异常可以不需要使用throws列举出来, 而编译异常一定要列举出来
异常的常用方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
public String getMessage() | 返回此 throwable 的详细信息字符串 |
public String toString() | 返回可抛出的简短描述。 |
public void printStackTrace() | 把异常错误输出到控制台中 |
java
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要求: number的长度小于等于10位, 将类型String转换为int类型
try {
//可能出现异常的代码
int result = method("1d3");
System.out.println(result);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//For input string: "1d3"
System.out.println(e.toString());//java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "1d3"
System.out.println("number数据不合法");
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
//手动处理异常问题
System.out.println("number的长度小于等于10位");
}
}
public static int method(String number) {
if(number.length() > 10) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
return Integer.parseInt(number);
}
}自定义异常
- 为什么需要自己写异常呢?
- 有些时候某个java自己写的异常无法满足我们的要求, 就需要自己写异常.
- 目的: 报错信息更加详细, 方便定位问题
- 书写格式:
XxxException
- 定义异常类
- 继承关系(如果是编译异常, 则继承
Exception; 如果是运行时异常, 则继承RuntimeException) - 空参构造
- 带参构造
java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Girlfriend girl = new Girlfriend();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("输入女朋友的姓名和年龄, 按照格式: 姓名 年龄. 姓名的长度在3-10之间, 年龄在18-40之间");
String s = sc.nextLine();
String[] arr = s.split(" ");
try {
girl.setName(arr[0]);
girl.setAge(Integer.parseInt(arr[1]));
} catch (NameFormatException | AgeFormatException e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
continue;
} catch (NumberFormatException | IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
//数组越界访问和类型转换问题都有格式导致
System.err.println("输入格式错误");
continue;
}
System.out.println(girl);
break;
}
}
}java
public class Girlfriend {
private String name;
private int age;
public Girlfriend() {
}
public Girlfriend(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
//姓名长度在3-10之间
if(name.length() < 3 || name.length() > 10) {
//抛出异常
throw new NameFormatException(name + "的长度没有在3-10之间");
}
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age < 18 || age > 40) {
throw new AgeFormatException(age + "不在18-40之间");
}
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "Girlfriend{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}java
public class NameFormatException extends RuntimeException {
public NameFormatException() {
}
//message在被捕获后, 通过getMessage()方法获取
public NameFormatException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}java
public class AgeFormatException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeFormatException() {
}
public AgeFormatException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}